Theme: Global Innovations in Sustainable Aquaculture, Fisheries
Biodiversity Congress 2018



Dear Colleagues,
On behalf of the Organizing Committee, it is an honor and pleasure to officially welcome you to the 7th International Conference on Biodiversity Conservation and Ecosystem Management, being held in Melbourne, Australia on July 26-27, 2018.
This Congress addresses key aspects of Biodiversity and brings together experts, researchers, private sector actors, postdoctoral fellows, and students from around the world, providing them with the opportunity to report, share, and discuss scientific questions, achievements, and challenges. We hope that participants will take the opportunity to network with others to find new ways to work toward the common goal of preserving the natural world and the ecosystem services it provides. We are also very interested in welcoming students and postdoctoral researchers in order to provide them the opportunity to learn and discuss their research at this event.
The theme of this conference, “Variety of Species Innovates Variety of Research” promises to address key issues within the broad field of biodiversity conservation and ecosystem management. Plenary, keynote, oral and poster presentation topics will include Sustainable Development, Climate Change, Threats to Biodiversity, Biodiversity and Food Security, Environmental Pollution and Management, and Plant, Animal and Marine Biodiversity.
I hope that this conference will stimulate new ideas and approaches for promoting ecosystem stability through preservation of biodiversity. I wish all delegates a fruitful attendance and involvement in this excellent event and hope that this conference will be productive and satisfying. Thank you for your participation, and I wish you a very enjoyable stay in Melbourne.
Dr. Ricky M. Bates
Professor of Horticulture
Penn State University
College of Agricultural Sciences An Equal Opportunity University
Conference Series llc LTD is a renowned organization that organizes highly notable conferences throughout the globe. Currently we are bringing forth “7th International Conference on Biodiversity Conservation and Ecosystem Management” (Biodiversity Congress 2018) scheduled to be held during July 26-27, 2018 Melbourne, Australia. The conference invites all the participants across the globe to attend and share their insights and convey recent developments and discoveries in the field of Biodiversity Conservation and Ecosystem Management.
2018 Highlights:
- 150+ Participation (70% Academia: 30% Industry)
- 6+ Keynote Speakers
- 20+ Plenary Speakers
- 4+ Exhibitors
- 19 Innovative Educational Sessions
- B2B Meetings
Target Audience:
- Ecologists
- Environmental Scientists
- Biologists
- Forestry Scientists
- Marine Scientists
- Fresh Water scientists
- Archaeologists
- Conservation Scientists


Conference Series llc LTD invites all the scholars from all over the world to attend and present their respective scientific research at '7th International Conference on Biodiversity Conservation and Ecosystem Management' during July 26-27, 2018 in Melbourne, Australia which includes prompt Keynote presentations, Oral talks, Poster presentations, Delegate views and Exhibitions.
Biodiversity Congress is a global platform to discuss and learn about Ecology and its associated fields, Evolution of Species, Plant & Animal Biodiversity, Biodiversity Management, Fauna & Flora, Biodiversity & Food Security, Conservation of Endangered Species, Marine Biodiversity, Forestry and Sustainable Energy Development.
Conference Series llc LTD Organizes 1000+ Global Events inclusive of 300+ International Conferences, 500+ Workshops and 200+ Symposiums every year across USA- Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific societies and publishes 400+ Open access journals which contains over 30000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Why to attend?
People from around the world are looking forward to build an Eco-friendly world and they are doing well with their research on different kind of species and how they evolved and diversified among the world and some of them were extinct and some of them are ready to extinct, which makes researchers to think and take care on conservation of endangered species. So we take an initiation to gather researchers from around the world at a single stage to discuss on the diversity of species and it’s relation with surrounding environment and also makes a strategy to conserve endangered species. We assure 7th International Conference on Biodiversity and Conservation is going to build a new enthusiasm among the people on importance of Biodiversity.
Target Audience:
· Ecologists
· Environmental Scientists
· Biologists
· Forestry Scientists
· Marine Scientists
· Fresh Water scientists
· Archaeologists
· Conservation Scientists
Conference Series llc LTD invites all the members of ecological family, from all over the world to join and share research at the '7th International Conference on Biodiversity Conservation and Ecosysytem Management' on July 26-27, 2018 at Melbourne, Australia which includes prompt keynote presentations, plenary talks, oral talks, poster presentations and exhibitions.
Theme: “Variety of Species Innovates Variety of Research”
Biodiversity Congress 2018 is providing a global platform to discuss and learn about our own ecology and its associated fields like evolution of species, plant & animal biodiversity, biodiversity management and its conservation, fauna & flora, biodiversity & food security, conservation of endangered species, marine biodiversity, forestry and sustainable energy development.
Track 1: Biodiversity
Across scales from genes to species, landscapes and biomes, biodiversity is an important resource for humanity. It is the key for a broad range of services provided by ecosystems. Biodiversity helps regulate the nutrient cycle, water (e.g. floods) and mitigates impacts of climate change. Biodiversity is also of direct importance for human well-being and for cultural and other values including recreation. The provisioning of clean water and diverse food supply makes it vital for all people.
Food security faces significant challenges due to population growth, poverty, globalization, climate change and other factors. Supplying healthy food to all citizens is crucial for global development - to reach it, not only food production but also equitable access to food for all people must be improved substantially. Biodiversity loss and global food security are hence two major challenges of our time. Linking these two areas from a research perspective, and seeking synergies between them is likely to generate multiple benefits for social, ecological and economic development.
Our "biodiversity event" focusing on Biodiversity & Food Security.
Related Conferences:
6th International Conference on Earth Science and Climate Change, September 18-19, 2017 Hong Kong; 3rd World Congress and Expo on Green Energy, September 28-29, 2017 Berlin, Germany; 2nd International Conference on Pollution Control and Sustainable Environment, October 5-6, 2017 London, UK; 3rd World Congress on Climate Change and Global Warming, October 16-17, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 4th World Congress on Renewable Biorefineries, October 16-17, 2017 Seoul, South Korea; International Conference on Biodiversity, Climate Change & Environmental Sciences, September 7-9, 2017, Tamilnadu, India; Third International Conference on Environment, Engineering and Energy, September 16-17, 2017, Toronto, Canada; 8th International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 7th International Conference on Environment and BioScience, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 9th International Conference on Research in Chemical, Agricultural, Biological and Environmental Sciences, November 27-28, 2017, Parys, South Africa
World Biodiversity Association Onlus, Biodiversity and Nature Conservation Association, Lao Biodiversity Association, FACE: The European Federation of Associations for Hunting & Conservation, UIA: Union of International Associations
Track 2: Sustainable Development
Living within our environmental limits is one of the central principles of sustainable development. One implication of not doing so is climate change. Environmental sustainable development involves making decisions and taking action that are in the interests of protecting the natural world, with particular emphasis on preserving the capability of the environment to support human life. Environmental sustainable development is about making responsible decisions that will reduce your business' negative impact on the environment. It is not simply about reducing the amount of waste you produce or using less energy, but is concerned with developing processes that will lead to businesses becoming completely sustainable in the future. Monitoring, analysis and management of environmental pollution in biodiversity Monitoring analysis and Assessment discusses technical developments and data arising from environmental monitoring and assessment, principles in the design of monitoring systems, and the use of monitoring data in assessing the consequences of natural resource management and pollution risks. Monitoring analysis designed to estimate exposure both at the individual and population levels, and also focuses on the development of monitoring systems related to the management of various renewable natural resources in, for instance, environment ,agriculture, fisheries and forests.
Our "biodiversity conferences" is providing a platform to speak on environmental issues.
Related Conferences:
3rd Annual Congress on Pollution and Global Warming, October 16-18, 2017 Atlanta, Georgia, USA; International Conference on Ecology and Ecosystems, September 18-20, 2017 Toronto, Ontario, Canada; 5th World Convention on Recycling and Waste Management, September 11-12, 2017 Singapore; 3rd World Congress on Climate Change and Global Warming, October 16-17, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 4th World Congress on Renewable Biorefineries, October 16-17, 2017 Seoul, South Korea; 7th International Conference on Environment and BioScience, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 9th International Conference on Research in Chemical, Agricultural, Biological and Environmental Sciences, November 27-28, 2017, Parys, South Africa; 5th International Conference on Sustainable Environment and Agriculture, October 28-30, 2017, Los Angeles, USA; 6th International Conference on Environment, Chemistry and Biology, November 20-22, 2017, Queensland, Australia
AMAZON Conservation Association, Ecological Society of America, NatureServe, Society of Conservation Biology, African Wild Dog Conservancy
Track 3: Climate Change and Global Warming
Biodiversity, short for biological diversity, is the term used to describe the variety of life found on Earth and all of the natural processes. . The different aspects of biodiversity all have a very strong influence on each other. It is helpful to think of an ecosystem as a woven carpet. Climate change is a major threat to biodiversity. Energy which is a major part of Biodiversity usually defined as the ability to do work. An energy system may be thought of as an interrelated network of Biodiversity and stores of energy, connected by transmission and distribution of that energy to where it is needed. The transformation from stores of energy in food to work and subsequent dissipation of energy is an example of such a system.
It is now widely recognized that biodiversity and climate change are interconnected. Biodiversity is affected by climate change, with negative consequences for human well-being, but biodiversity, through the ecosystem services it supports, also makes an important contribution to both climate change mitigation and adaptation. Conserving natural terrestrial, freshwater and marine ecosystems and restoring degraded ecosystems (including their genetic and species diversity) is essential for the overall goals of both the Convention on Biological Diversity and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change because ecosystems play a key role in the global carbon cycle and in adapting to climate change, while also providing a wide range of ecosystem services that are essential for human well-being and the achievement of the Millennium Development Goals.
Our [biodiversity conferences] is providing a platform to speak much more on Biodiversity & Climate Change.
Related Conferences:
2nd International Conference on Pollution Control and Sustainable Environment, October 5-6, 2017 London, UK; 3rd World Congress on Climate Change and Global Warming, October 16-17, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 4th World Congress on Renewable Biorefineries, October 16-17, 2017 Seoul, South Korea; 4th World Congress and Expo on Recycling, July 27-29, 2017 Rome, Italy; 6th International Conference on Recycling: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, November 6-8, 2017 Las Vegas, Nevada, USA; Third International Conference on Environment, Engineering and Energy, September 16-17, 2017, Toronto, Canada; 8th International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 7th International Conference on Environment and BioScience, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 9th International Conference on Research in Chemical, Agricultural, Biological and Environmental Sciences, November 27-28, 2017, Parys, South Africa; 5th International Conference on Sustainable Environment and Agriculture, October 28-30, 2017, Los Angeles, USA
BirdLife Australia, The Earth Organization, International Anti-Poaching Foundation, The Nature Conservancy, Wild Salmon Center
Track 4: Ecology and Biodiversity Conservation
Ecosystem functioning reflects the collective life activities of plants, animals, and microbes and the effects these activities feeding, growing, moving, excreting waste, etc. have on the physical and chemical conditions of their environment. (Note that functioning means showing activity and does not imply that organisms perform purposeful roles in ecosystem-level processes.) A functioning ecosystem is one that exhibits biological and chemical activities characteristic for its type. Ecologists abstract the essential features of an ecosystem into two compartments, the biotic and the abiotic. The biotic compartment consists of the community of species, which can be divided functionally into plant producers, the consumers that feed on producers and on each other, and the decomposers. The abiotic compartment consists of organic and inorganic nutrient pools. Energy and materials move between these two compartments, as well as into and out of the system. Comparing different ecosystems is likely to yield an unclear result because the response to variations in biodiversity cannot easily be distinguished from responses caused by variations in environmental and other factors. [biodiversity conferences USA] explained very well about Biodiversity & Ecosystem.
Related Conferences:
4th World Congress and Expo on Recycling, July 27-29, 2017 Rome, Italy; 6th International Conference on Recycling: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, November 6-8, 2017 Las Vegas, Nevada, USA; 4th World Conference on Climate Change, October 19-21, 2017 Rome, Italy; 3rd Annual Congress on Pollution and Global Warming, October 16-18, 2017 Atlanta, Georgia, USA; International Conference on Ecology and Ecosystems, September 18-20, 2017 Toronto, Ontario, Canada; 5th International Conference on Sustainable Environment and Agriculture, October 28-30, 2017, Los Angeles, USA; 6th International Conference on Environment, Chemistry and Biology, November 20-22, 2017, Queensland, Australia; International Conference on Biodiversity, Climate Change & Environmental Sciences, September 7-9, 2017, Tamilnadu, India; Third International Conference on Environment, Engineering and Energy, September 16-17, 2017, Toronto, Canada; 8th International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea
FACE: The European Federation of Associations for Hunting & Conservation, UIA: Union of International Associations, AMAZON Conservation Association, Ecological Society of America, NatureServe
Track 5: Plant and Animal Biodiversity
Plants define the habitat of a site, providing structure, shelter and food as well as contributing to the overall biodiversity. Plants are a kingdom of life forms that includes familiar organisms such as trees, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns and mosses. Through photosynthesis, they convert water and carbon dioxide into the oxygen we breathe and the sugars that provide the primary fuel for life. Plants were instrumental to evolution as a whole in that they produced the oxygen that made life on Earth possible — not only by "breathing" it into the atmosphere and transforming it, but also by crushing rocks with their roots, which created soils and released nutrients on a large scale. Plant diversity is well represented in rural areas, development pressures have reduced the amount of green space in urban and peri-urban areas, resulting in a poorer diversity of plant communities. However, there are still many small pockets of green space within the built environment with a rich diversity of plant species, and other areas where improvements to green space could encourage the establishment of plants. Management of urban green space directly influences the micro-environment and can create conditions favorable to a range of plants, which in turn can increase habitats for, and therefore the diversity of, other species groups.
How animals have adapted to survive and thrive in their environmental riches? is one of the most fascinating aspects of biology. Farm animal biodiversity is important for maintaining genetically diverse and healthy livestock. However, this diversity is being threatened by industrial farming operations that depend on a small number of farm animal breeds that can thrive in an intensive livestock environment. Because of this, farm animal breeds that don't thrive in factory farming operations are becoming more rare.
Variability is essential for the evolution and adaptation of living organisms, including animals be they wild or domestic, and constitutes a vast field of research. Such research will lead a better understanding of the ecosystems and the discovery of various molecules with potential benefits to the humanity. biodiversity Protection is therefore crucial both for animals and humans, in particular at a time when global challenges are posed by growing human population; increasing movement of goods, animals and people, together with pathogens and invasive species; and climate changes, to name a few.
Previous biodiversity conferences 2017 explained the importance of Plant and Animal Biodiversity and it’s conversation as well.
Related Conferences:
3rd World Congress and Expo on Green Energy, September 28-29, 2017 Berlin, Germany; 2nd International Conference on Pollution Control and Sustainable Environment, October 5-6, 2017 London, UK; 3rd World Congress on Climate Change and Global Warming, October 16-17, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 4th World Congress on Renewable Biorefineries, October 16-17, 2017 Seoul, South Korea; 4th World Congress and Expo on Recycling, July 27-29, 2017 Rome, Italy; 9th International Conference on Research in Chemical, Agricultural, Biological and Environmental Sciences, November 27-28, 2017, Parys, South Africa; 5th International Conference on Sustainable Environment and Agriculture, October 28-30, 2017, Los Angeles, USA; 6th International Conference on Environment, Chemistry and Biology, November 20-22, 2017, Queensland, Australia; 8th International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 7th International Conference on Environment and BioScience, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea
Ecological Society of America, NatureServe, Society of Conservation Biology, African Wild Dog Conservancy, BirdLife Australia
Track 6: Marine Biodiversity
Biodiversity is now commonly defined as the variety of life in genes, species and habitats. According to the definition of the Convention on Biological Diversity, biodiversity is the variability among living organisms from all sources, including inter alia, terrestrial, marine and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes of which they are part; this includes diversity within species, between species and of ecosystems. The three domains of life, bacteria, archaea and eukarya are present in the marine environment. In addition there are viruses. About 230,000 species of marine plants and animals have been scientifically described and a few thousand bacteria and archaea. This known biodiversity only represents a small fraction of the number of species existing, except for the macrophytes and seagrasses which are living in coastal environments and, in general, for the pelagic environment. Species diversity in the oceanic pelagic environment is extremely low. Habitat diversity and the number of marine habitats are difficult to define. Studies of zonation have typically demonstrated the existence of very narrow zones in intertidal areas, where direct observation is possible, and broader and broader zones as one goes deeper. Marine ecosystems deliver a series of services that are essential to the proper functioning of the Earth. These include the production and mineralization of organic material, the storage of carbon, the storage of pollutants and waste products from land, the buffering of the climate and of climate change, coastal protection (mangroves, dune-beach systems, coral reefs). Most of these services are delivered by microscopic organisms.
Marine Biodiversity research an important product of marine biodiversity research should be the necessary knowledge and tools for adequately managing and protecting marine biodiversity. This requires knowledge on genetic and ecological mechanisms that control biodiversity (gene flow, dispersal, adaptive value of genetic polymorphisms, determination of dispersal and recruitment, species interactions including invasions, sediment transport, natural and human-induced catastrophes, etc.). It also requires knowledge on the functional role of biodiversity.
Marine biodiversity research can discuss only at [biodiversity conferences]
Related Conferences:
3rd World Congress on Climate Change and Global Warming, October 16-17, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 4th World Congress on Renewable Biorefineries, October 16-17, 2017 Seoul, South Korea; 4th World Congress and Expo on Recycling, July 27-29, 2017 Rome, Italy; 6th International Conference on Recycling: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, November 6-8, 2017 Las Vegas, Nevada, USA; 4th World Conference on Climate Change, October 19-21, 2017 Rome, Italy; International Conference on Biodiversity, Climate Change & Environmental Sciences, September 7-9, 2017, Tamilnadu, India; Third International Conference on Environment, Engineering and Energy, September 16-17, 2017, Toronto, Canada; 8th International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 7th International Conference on Environment and BioScience, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 9th International Conference on Research in Chemical, Agricultural, Biological and Environmental Sciences, November 27-28, 2017, Parys, South Africa
World Biodiversity Association Onlus, Biodiversity and Nature Conservation Association, Lao Biodiversity Association, FACE: The European Federation of Associations for Hunting & Conservation, UIA: Union of International Associations
Track 7: Forestry
Flora is the plant life occurring in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring or indigenous, native plant life and Fauna is all of the animal life of any particular region or time. Both are collective terms, referring to groups of plant or wildlife specific to a region or a time period.
To geographical groupings, environment also helps further their classification. For example, aquatic flora and fauna of a region refers to the plant and animal life found in the waters in or surrounding a geographic region.
Conservation, The area of flora, fauna and biodiversity is quite interrelated. Flora and fauna forms a major part of biodiversity. India is a land of varied flora, fauna and biodiversity. India is one of the twelve mega-diverse nations of the World. Two of India's great mountain ranges, the Eastern Himalayas and the Western Ghats have been designated among the world's eighteen 'hotspots' of biodiversity. But In the last few decades we have seen a steady increase in the extinction rate of flora, fauna etc. all over world including India and so now, conservation of biological diversity is of paramount importance to the survival of man. Conservation of biological diversity leads to conservation of essential ecological diversity to preserve the continuity of food chains. The genetic diversity of plants and animals is preserved. It ensures the sustainable utilization of life support systems on earth. It provides a vast knowledge of potential use to the scientific community. A reservoir of wild animals and plants is preserved, thus enabling them to be introduced, if need be, in the surrounding areas. Biological diversity provides immediate benefits to the society such as recreation and tourism. Biodiversity conservation serves as an insurance policy for the future.
The major role of Forest in our ecosystem was explained at biodiversity conferences 2017
Related Conferences:
6th International Conference on Earth Science and Climate Change, September 18-19, 2017 Hong Kong; 3rd World Congress and Expo on Green Energy, September 28-29, 2017 Berlin, Germany; 2nd International Conference on Pollution Control and Sustainable Environment, October 5-6, 2017 London, UK; 3rd World Congress on Climate Change and Global Warming, October 16-17, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 4th World Congress on Renewable Biorefineries, October 16-17, 2017 Seoul, South Korea; International Conference on Biodiversity, Climate Change & Environmental Sciences, September 7-9, 2017, Tamilnadu, India; Third International Conference on Environment, Engineering and Energy, September 16-17, 2017, Toronto, Canada; 8th International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 7th International Conference on Environment and BioScience, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 9th International Conference on Research in Chemical, Agricultural, Biological and Environmental Sciences, November 27-28, 2017, Parys, South Africa
AMAZON Conservation Association, Ecological Society of America, NatureServe, Society of Conservation Biology, African Wild Dog Conservancy
Track 8: Vulnerable species
Conservation of Endangered Species is done by Captive breeding Captive breeding is the process of breeding rare or endangered species in human controlled environments with restricted settings, such as wildlife preserves, zoos and other conservation facilities. Captive breeding is meant to save species from extinction and so stabilize the population of the species that it will not disappear. Additionally, if the captive breeding population is too small, then inbreeding may occur due to a reduced gene pool and reduce immunity. In 1981, the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA) created a Species Survival Plan (SSP) in order to help preserve specific endangered and threatened species through captive breeding and Private farming
Where poaching substantially reduces endangered animal populations, legal, for-profit, private farming does the opposite. It has substantially increased the populations of the southern black rhinoceros and southern white rhinoceros. Recovery Plans In the United States and many other countries, recovery plans are often developed to aid in the recovery of the species. These recovery programs can be in situ (take place in the natural range of the species) or ex situ (in areas outside their natural range) and can involve. Even our international conference on biodiversity 2017 concentrated mostly on Endangered Species.
Related Conferences:
3rd Annual Congress on Pollution and Global Warming, October 16-18, 2017 Atlanta, Georgia, USA; International Conference on Ecology and Ecosystems, September 18-20, 2017 Toronto, Ontario, Canada; 5th World Convention on Recycling and Waste Management, September 11-12, 2017 Singapore; 3rd World Congress on Climate Change and Global Warming, October 16-17, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 4th World Congress on Renewable Biorefineries, October 16-17, 2017 Seoul, South Korea; 7th International Conference on Environment and BioScience, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 9th International Conference on Research in Chemical, Agricultural, Biological and Environmental Sciences, November 27-28, 2017, Parys, South Africa; 5th International Conference on Sustainable Environment and Agriculture, October 28-30, 2017, Los Angeles, USA; 6th International Conference on Environment, Chemistry and Biology, November 20-22, 2017, Queensland, Australia
Ecological Society of America, NatureServe, Society of Conservation Biology, African Wild Dog Conservancy, BirdLife Australia
Track 9: Threats to Biodiversity
Biodiversity is under serious threat as a result of human activities. The main dangers worldwide are population growth and resource consumption, climate change and global warming, habitat conversion and urbanisation, invasive alien species, over-exploitation of natural resources and environmental degradation. Species often become threatened or disappear when several of these factors are combined. The fragmentation of habitats decreases the size of populations and makes these more vulnerable to other factors.
Threats to biodiversity can discuss and invent a proper method only at [biodiversity conferences]
Related Conferences:
2nd International Conference on Pollution Control and Sustainable Environment, October 5-6, 2017 London, UK; 3rd World Congress on Climate Change and Global Warming, October 16-17, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 4th World Congress on Renewable Biorefineries, October 16-17, 2017 Seoul, South Korea; 4th World Congress and Expo on Recycling, July 27-29, 2017 Rome, Italy; 6th International Conference on Recycling: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, November 6-8, 2017 Las Vegas, Nevada, USA; Third International Conference on Environment, Engineering and Energy, September 16-17, 2017, Toronto, Canada; 8th International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 7th International Conference on Environment and BioScience, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 9th International Conference on Research in Chemical, Agricultural, Biological and Environmental Sciences, November 27-28, 2017, Parys, South Africa; 5th International Conference on Sustainable Environment and Agriculture, October 28-30, 2017, Los Angeles, USA
Society of Conservation Biology, African Wild Dog Conservancy, BirdLife Australia, The Earth Organization, International Anti-Poaching Foundation
Track 10: Biodiversity and Food Security
Healthy ecosystems are essential to increase resilience and agricultural production in the face of change.
Production needs to be sustainable: capitalizing on biological processes and harvesting resources without compromising natural capital such as biodiversity and ecosystem services.
A large number of the world’s poor rely directly on biodiversity and ecosystem services, and their livelihoods would be affected first and foremost by biodiversity loss.
A vastly broader share of the human population would be affected by a decrease in the provision of ecosystem services related to food production, nutrition, water and sanitation.
The major role of Food in our ecosystem was explained well at biodiversity conferences 2017
Related Conferences:
3rd World Congress on Climate Change and Global Warming, October 16-17, 2017 Dubai, UAE; 4th World Congress on Renewable Biorefineries, October 16-17, 2017 Seoul, South Korea; 4th World Congress and Expo on Recycling, July 27-29, 2017 Rome, Italy; 6th International Conference on Recycling: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, November 6-8, 2017 Las Vegas, Nevada, USA; 4th World Conference on Climate Change, October 19-21, 2017 Rome, Italy; International Conference on Biodiversity, Climate Change & Environmental Sciences, September 7-9, 2017, Tamilnadu, India; Third International Conference on Environment, Engineering and Energy, September 16-17, 2017, Toronto, Canada; 8th International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 7th International Conference on Environment and BioScience, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea; 9th International Conference on Research in Chemical, Agricultural, Biological and Environmental Sciences, November 27-28, 2017, Parys, South Africa
BirdLife Australia, The Earth Organization, International Anti-Poaching Foundation, The Nature Conservancy, Wild Salmon Center
Track 11: Environmental Pollution & Management
The Biodiversity Management Branch is responsible for the conservation and restoration of biodiversity within the City's boundary. A fundamental aspect to the branch’s work is to ensure that biodiversity and nature are mainstreamed into everyday life, which includes delivering tangible benefits to all communities. More specifically, this Biodiversity Management branch is responsible for conservation planning, biodiversity management and alien species eradication. In the field of conservation planning, the City’s approved Biodiversity Strategy has resulted in the identification of a biodiversity network of sites that need to be secured to conserve a representative sample of the Cape Town’s unique biodiversity and, thus, promote sustainable development. Key functions of the Biodiversity Management branch include:
· Nature reserve management
· Biodiversity strategy co-ordination
· Monitoring and evaluation
· Protected area status
· Invasive alien species co-ordination
We have seen a great response on Biodiversity Management at biodiversity conference 2017
Related Conferences:
4th World Congress and Expo on Recycling, July 27-29, 2017 Rome, Italy; 6th International Conference on Recycling: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, November 6-8, 2017 Las Vegas, Nevada, USA; 4th World Conference on Climate Change, October 19-21, 2017 Rome, Italy; 3rd Annual Congress on Pollution and Global Warming, October 16-18, 2017 Atlanta, Georgia, USA; International Conference on Ecology and Ecosystems, September 18-20, 2017 Toronto, Ontario, Canada; 5th International Conference on Sustainable Environment and Agriculture, October 28-30, 2017, Los Angeles, USA; 6th International Conference on Environment, Chemistry and Biology, November 20-22, 2017, Queensland, Australia; International Conference on Biodiversity, Climate Change & Environmental Sciences, September 7-9, 2017, Tamilnadu, India; Third International Conference on Environment, Engineering and Energy, September 16-17, 2017, Toronto, Canada; 8th International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry, October 11-13, 2017, Busan, South Korea
World Biodiversity Association Onlus, Biodiversity and Nature Conservation Association, Lao Biodiversity Association, FACE: The European Federation of Associations for Hunting & Conservation, UIA: Union of International Associations
Summary of Biodiversity Conference:
Biodiversity conference series is playing an important role to create awareness and providing a platform to share and discuss on, how different types of species evolved in our ecology and about its importance and how to be eco-friendly to eradicate the word extinction. World is looking at extinction of species, so we are organizing series of biodiversity conferences which mainly aims to invent a method on extinction of endangered species. We are inviting the whole world to gather at a single platform and to raise-up their voice on our own “Biodiversity”.
Scope and Importance of Biodiversity Research:
Biodiversity is the variation of life on earth. Biodiversity encompasses of microorganisms, plants, animals, ecosystems such as coral reefs, forests, rain forests, deserts etc. In a whole it includes unicellular to multicellular and surrounding environment. The study and research on biodiversity is unlimited. The scope of biodiversity includes ecology, evolution, marine science, animal science, plant science, landscape, environmental science, geology, forestry, sustainable energy, medicinal field etc.
The importance of biodiversity research is to evaluate the different kinds of species among our biosphere and helps to find new ways for the conversation of endangered species and to prevent upcoming threats of imbalance in the ecosystem. Up to now we have several types of species in our ecology and the research which is going-on will give much more varieties of species and its evolution as well, so we came up with a theme “Variety of Species Innovates Variety of Research”
About Australia:
Melbourne is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in Australia and Oceania. The metropolis is located on the large natural bay of Port Phillip and expands into the hinterlands towards the Dandenong and Macedon mountain ranges, Mornington Peninsula and Yarra Valley. Melbourne rates highly in education, entertainment, health care, research and development, tourism and sport, making it the world's most liveable city for the sixth year in a row in 2016, according to the Economist Intelligence Unit. It is a leading financial center in the Asia-Pacific region, and ranks among the top 30 cities in the world in the Global Financial Centers Index.
Melbourne's multicultural atmosphere is set amongst Victorian-era buildings and gorgeous parkland. It has a population of just over 4 million people, and is a picturesque place with so much to offer the visitor and resident alike. The city center, also known as the Central Business District (CBD), is on the north bank of the Yarra River. It is approximately 5 kilometers inland from Port Phillip Bay, where most of the pretty suburbs are situated. The heart of the city is marked by Bourke Street Mall which is situated between Swanston Street and Elizabeth Street, running north to south. Bourke Street and Collins Street are the main roads running west to east. One of the best ways to really enjoy Melbourne is to take part in an organized tour. Some of the popular ones include the Great Ocean Road Tour and for the adventurous Caving is also popular.
Why is it Melbourne, Australia?
Australia is one of seventeen countries described as being 'mega diverse'. This group of countries has less than 10% of the global surface, but support more than 70% of the biological diversity on earth. Australia is home to between 600,000 and 700,000 species, many of which are endemic, that is they are found nowhere else in the world. These include, for example, 84% of our plant species, 83% of mammals, and 45% of birds. Australia's biodiversity - the plants, animals, micro-organisms and their ecosystems - is threatened from the impacts of human activities. Since European settlement, more than 50 species of Australian animals and over 60 species of Australian plants are known to have become extinct.
Australia has more than 1,700 species and ecological communities are known to be threatened and at risk of extinction. Degradation of our environment continues and many ecosystems are increasingly vulnerable to collapse. Australia’s biodiversity is declining because of the impacts of a range of threats, including: habitat loss, degradation and fragmentation; invasive species; unsustainable use and management of natural resources; changes to the aquatic environment and water flows; changing fire regimes; Climate change.
Lost biodiversity can never be fully recovered, but through our conservation efforts we can help to ensure that species are able to persist and to restore the capacity of ecosystems to adapt to changes and disturbances—in other words, to build ecological resilience.
Environment:
Environmental sustainability is the basis of all Future Melbourne goals. Majorly requires current generations to choose how they meet their needs without compromising the ability of future generations to be able to do the same. The city’s urban ecology must be designed and managed as a dynamic whole to balance the interdependencies between its flora and fauna, microclimate, water cycles and its human, social and economic infrastructure.
Melbourne is rated high in education, entertainment, health care, research and development, tourism and sport, making it the world's most liveable city for the seventh year in a row in 2017, according to the Economist Intelligence Unit. It is a leading financial Centre in the Asia-Pacific region, and ranks among the top 30 cities in the world in the Global Financial Centers Index. Referred to as Australia's "cultural capital", it is the birthplace of Australian impressionism, Australian rules football, the Australian film and television industries, and Australian contemporary dance. It is recognized as a UNESCO City of Literature and a major Centre for street art, music and theatre. It is home to many of Australia's largest and oldest cultural institutions such as the Melbourne Cricket Ground, the National Gallery of Victoria, the State Library of Victoria and the UNESCO World Heritage-listed Royal Exhibition Building.
Population:
According to Australia census, the top five ancestries for people in Melbourne are: English, Australian, Irish, Scottish and Italian. The top five languages (other than English) spoken in Melbourne are: Italian, Greek, Mandarin, Vietnamese and Cantonese. The top six countries of birth for people in Melbourne are: Australia, England, India, China, New Zealand, and Italy.
Melbourne is the capital city of Victoria with a population of over 4.5 million which accounts for 19.05% of national population. It ranks second most populated state in Australia after Sydney. Melbourne is Victoria’s business, administrative, cultural and recreational hub of the state. On an average day around 854, 000 people use the city, and each year Melbourne hosts over a million international visitors.
Climate:
Melbourne, the state capital of Victoria and second largest city in Australia, has a temperate oceanic climate. This is mainly due to Melbourne's geographical location. This temperature differential is most pronounced in the spring and summer months and can cause very strong cold fronts to form. These cold fronts can be responsible for all sorts of severe weather from gales to severe thunderstorms and hail, minor temperature drops, and heavy rain.
Weather:
Melbourne enjoys warm summers, glorious springs, mild autumns and crisp winters. With its variable climate, Melbourne heats up from December to February (summer), cools down March to May (autumn), chills out June to August (winter), and warms up back again from September to November (spring). Melbourne's top temperatures are usually in January and February. Those months are often dry, with hot spells and cooling afternoon breezes off Port Phillip Bay. June and July are the coldest months, and October is the wettest. Annual average rainfall in Melbourne is around 650mm it is less wet than Sydney.
Energy:
Australia uses a number of fuels or technologies, including coal, natural gas and renewable energy sources - hydro, wind and solar for energy generation. Brown coal is the primary energy source in the generation of electricity in the State of Victoria, Australia. Brown coal is also one of the largest contributors for Australia's total domestic greenhouse gas emissions and a source of huge controversy for the country. Australia is one of the highest polluters of greenhouse gas per capita in the world. Brown coal is used for the generation of approximately 85% of Victoria's household, commercial and industrial electricity consumption.
Members associated with Biodiversity Research:
There are about 25 universities are working on Biodiversity, along with some associations, societies and government organizations. People involved are doctorates, post doc’s, Ph. D scholars and post graduates.
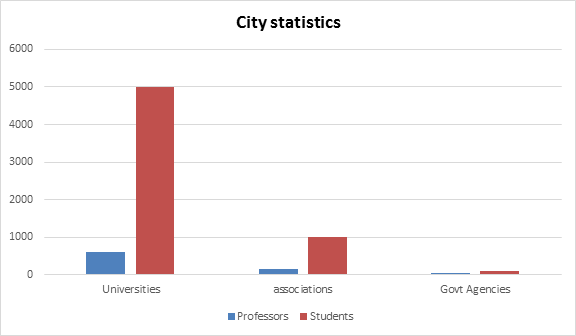
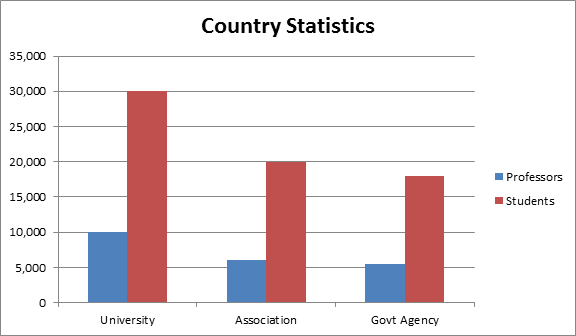
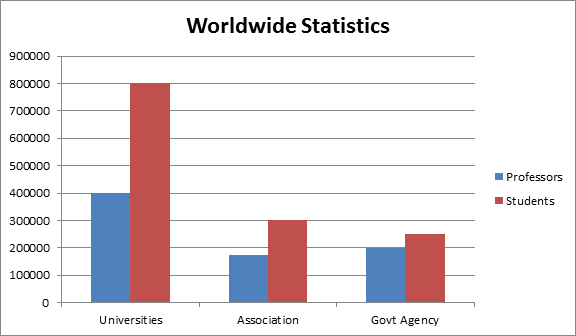
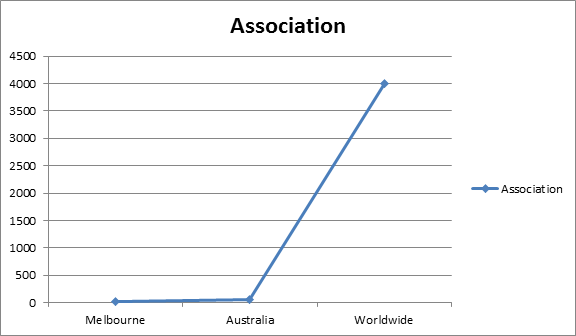
Societies Associated with Biodiversity Research:
The below listed are some of the societies or associations working on Biodiversity and its conservation
· Australian Conservation Foundation
· Australian Network of Environmental Defenders Offices (ANEDO)
· Greenpeace Australia Pacific
· Sustainable Population Australia
· Australian Garden History Society
· Conservation Volunteers Australia
· Australian Conservation Foundation
· Australian Conservation Foundation Inc.
· Tree Project Inc
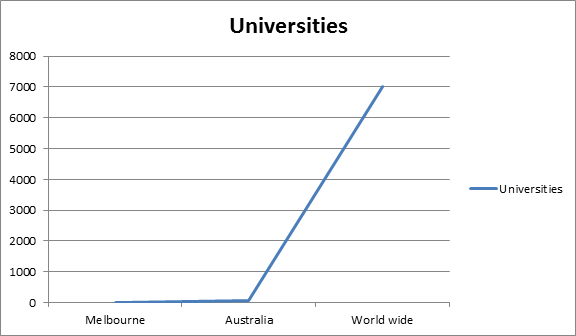
Universities Associated with Biodiversity Research:
Melbourne has around 25 universities, in which Biodiversity research works are carried out extensively. The below listed are some of the universities
· University of Melbourne
· LA TROBE University
· University of Tasmania
· Charles Sturt University
· Monash University
· Victoria University
· University of Wollongong
· Deakin University
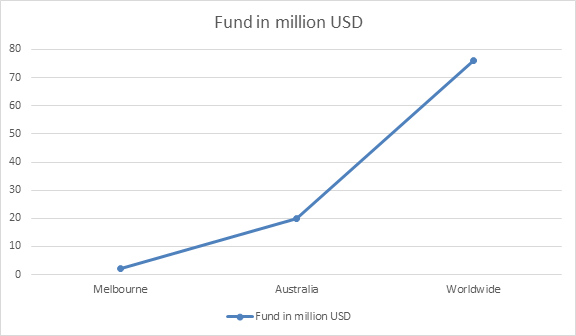
Market Value on Biodiversity Research:
A huge amount of grants is provided for research on Biodiversity and Environment science related research. The NESP funding of $145 million over the six years from 2015 to 2021 supports six themed research hubs, along with projects to address emerging environmental research needs. The National Land Care Program's new Smart Farming Partnerships is offering multi-year grants of between $250,000 and $4 million to put in place new and innovative sustainable land management practices, which protect and improve the condition of Land.
The Coalition Government is continuing its longstanding commitment to natural resource management, investing more than $1 billion for phase two of the National Land Care Program. Community information sessions on Regional Land Partnerships and Smart Farms Program will be held in selected cities from 9 October 2017. The Australian Government has committed $210 million to the Reef Trust to provide innovative, targeted investment focused on improving water quality, restoring coastal ecosystem health and enhancing species protection in the Great Barrier Reef region. The Australian Government has mobilized over $210 million in support of threatened species since 2014. 20 million trees will be planted by 2020 to deliver real environmental benefits at the local level. Along with these organization many other organizations and association are funding for research on Biodiversity.
Market Growth of Biodiversity Research in the last and upcoming ten years:
New market mapping reveals the growth of eco market. Environmental markets aim to support conservation by putting a price on the ecosystem services nature provides, such as clean water and stored carbon. The new atlas was developed in collaboration with the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Office of Environmental Markets (OEM) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). It charts the progression of ecosystem markets since the 1980s, and the accompanying report identifies market trends. The DOI launched a Natural Resource Investment Center to enhance private investment in wetland and species mitigation. In August, the EPA and USDA released a report pledging support to water quality trading markets in various ways. The White House’s efforts to spur private investment in conservation show signs of success. In March, 11 organizations — some public, though mostly private — committed over $2 billion to water, wildlife and land investments. It’s a commitment that the White House quickly labeled one of the biggest non-federal investments in conservation ever.
Funding Opportunities:
The total amount offered under the Environmental Research program in 2017 will be $1,000,000. Societies like Australian Research Council funds for research on Biodiversity, it grants $33,750,000 for research on Biodiversity and Ecology. Huge grants are provided by foundations like Safari Club International Foundation, Nature Foundation of SA, Australian Biological Resources Study.
References:
· http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/conservation/hotspots
· http://www.population.net.au/melbourne-population/
· https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Climate_of_Melbourne
· http://www.visitvictoria.com/Information/Melbourne-weather
· http://www.melbourne.vic.gov.au/about-council/vision-goals/eco-city/Pages/eco-city.aspx
· https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_environmental_research_institutes
· https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Environment_of_Australia
· http://www.environment.gov.au/about-us/grants-funding
· https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Funding_of_science
Conference Highlights
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | July 26-27,2018 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||